Struggling with a poor Wi-Fi signal? Here are some ways you can boost your speeds.
The challenges of slow browsing, streaming difficulties, dropped Wi-Fi signals, and wireless dead zones can be immensely frustrating in the contemporary world where internet access is deemed as vital as any other basic requirement. Although not as fundamental as breathing, it still holds significant importance for many.
If you are experiencing sluggish Wi-Fi, several tools can assist in testing your internet speed, while a few troubleshooting techniques can help address network problems. In the event that standing next to your wireless router is the only way to get decent reception, implementing some simple tips can help optimize your network and improve its performance. We’ll review these tips for increasing your Wi-Fi signal below.
Opt for a VPN
One of the top ways you can improve internet speeds is with a VPN. Many of these providers have top speeds that you maybe can't obtain from your ISP. When you connect to their servers, you'll have improved internet browsing, streaming, downloading, and more.
The challenge is finding a VPN provider that will suit your needs. While there are some free ones, they are limited in how many countries you can connect to with slow speeds. If you want ultimate performance, you'll sadly have to pay for it. Fortunately, there are some VPNs that stand out above the rest, and I recommend you try one of these:
Here are some other options you can try at home if the VPN service isn't boosting speeds at much as you thought.
Test your internet connection
Don't be too quick to blame your Wi-Fi if you're experiencing slow browsing. First, ensure that your internet connection is functioning correctly by directly connecting your computer to the router using an Ethernet cable. If your laptop lacks an Ethernet port, don't worry! Just get yourself a USB-to-Ethernet adapter.
Next, run a speed test to determine your internet speed. If the speed doesn't match what you're paying for, it's time to call your ISP or replace your modem or router. However, if the speed test does match your internet bill, but your internet still seems slow, it might be worth upgrading to a better plan.
If everything checks out, try running the test again wirelessly while standing right next to the router. If you get good speeds next to the router, but experience connectivity issues elsewhere in the house, it's possible that your Wi-Fi coverage is to blame. But if your internet is still slow while standing right next to the router, it might be time to upgrade your equipment.
Update your router’s firmware
Before you start making any changes to your Wi-Fi setup, consider updating your router's firmware. Router manufacturers are always working on improving their software to enhance performance. The process of upgrading your firmware can be simple or complicated, depending on your device's manufacturer and model.
Most modern routers have the firmware update process built into the administration interface, so all you need to do is press a firmware upgrade button. However, older models may require you to visit the manufacturer's website, download a firmware file from your router's support page, and then upload it to the administration interface. While this may be a tedious process, updating your firmware can often provide a simple solution to any issues you may be experiencing.
In fact, it's advisable to update your firmware regularly, even if your wireless network is working fine. This ensures that you benefit from performance improvements, new features, and security updates. If you need assistance with this, we have a guide on how to access your router's settings.
If you're looking to optimize your router's performance further, you could consider using a third-party firmware such as the open-source DD-WRT. This option can provide you with access to more advanced networking features, including the ability to install a VPN directly onto your router. While it may be a bit more complex to set up, tech-savvy users may find it to be worthwhile.
Find the best location for your router
It's essential to understand that not all homes distribute Wi-Fi signals equally. The placement of your router can significantly impact your wireless coverage. While it may seem reasonable to keep the router inside a cabinet or close to the window where the cable comes in, it's not always the best option. Here are some tips to ensure optimal placement:
- Keep your wireless router in an open space, away from walls and obstructions to avoid interference and overheating.
- If possible, place the router in the center of your house to enable the signal to reach every corner of your home effortlessly.
- Eliminating even one wall between your workspace and the router can significantly enhance the performance of your Wi-Fi network.
- Avoid using heavy-duty appliances or electronics near the router, as they can negatively affect Wi-Fi performance.
- If your router has external antennas, orient them vertically to extend your network's coverage.
- Elevating your router by mounting it high on a wall or on the top shelf can also help to improve signal strength.
Several tools are available to help you visualize your network coverage. Ekahau's Heatmapper or MetaGeek's inSSIDer are excellent options that identify the weak and strong spots in your Wi-Fi network. Additionally, mobile apps such as Netgear's WiFi Analytics can be useful for this purpose.
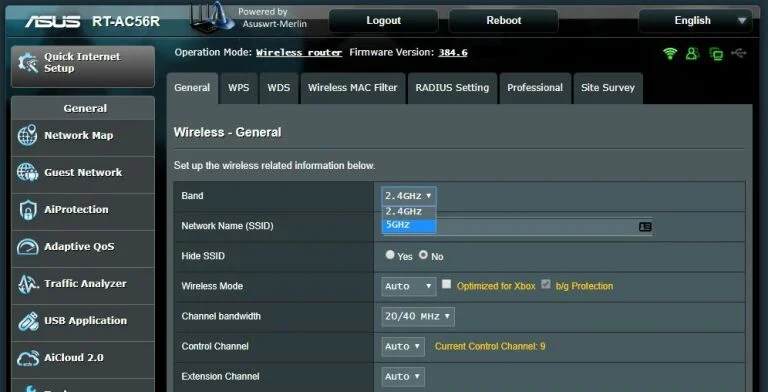
Check your frequency
To ensure optimal performance of your network, it's recommended to check your network's administrator interface and configure it accordingly. If you have a dual-band router, you may obtain better throughput by switching to the 5GHz band instead of the more commonly used 2.4GHz band.
The 5GHz band offers faster speeds and is less likely to be impacted by interference from other wireless networks and devices due to its less frequent use. However, it may not reach as far or handle obstructions and distances as efficiently as the 2.4GHz signal.
Most modern dual-band routers allow you to use the same network name or SSID on both bands. Check your router's administration interface for the 5GHz network option and use the same SSID and password as your 2.4GHz network. This ensures that your devices will automatically select the best signal available.
If your router does not provide an option to use the same SSID, give the 5GHz network a distinct name and try to connect to it manually whenever possible.
Related: Wi-Fi 7 - The future of wireless networking
Change the channel
Wireless signal interference can be a significant issue, especially for individuals residing in densely populated areas. The impact can be felt not only from other wireless networks but also from cordless phone systems, microwaves, and other electronic devices.
Do you recall playing with walkie-talkies as a child? The units had to be on the same "channel" for you to communicate with each other. Even if someone else was using a completely different set, if they were on the same channel as your neighbor, you could eavesdrop on their conversation. Similarly, modern routers can switch across various channels when communicating with your devices.
While most routers automatically choose the best channel for you, signal congestion can occur if neighboring wireless networks use the same channel. A high-quality router set to "Automatic" mode will attempt to choose the least congested channel. However, older or less expensive routers may select a predefined channel, even if it is not the most suitable one, resulting in problems with your wireless network's performance.
If you're using a Windows PC, you can determine the channels neighboring Wi-Fi networks are using. Open the command prompt and type "netsh wlan show all." This will display a list of all wireless networks and the channels being used in your vicinity. Additionally, network analyzers can also present this information in an easy-to-read graphical format.
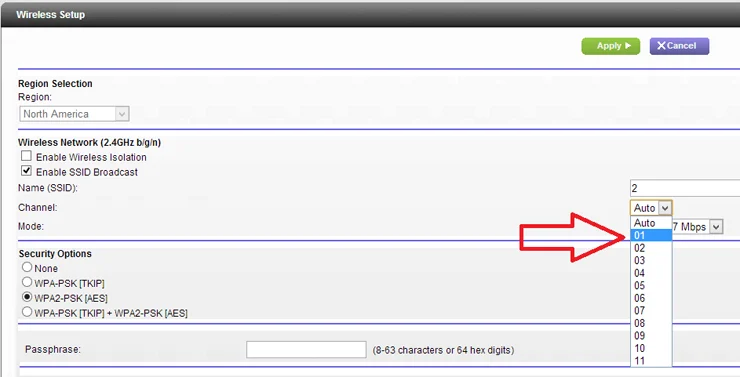
For 2.4GHz, it's best to use channels 1, 6, and 11 since they don't overlap with other channels, which can reduce performance. In contrast, 5GHz typically utilizes non-overlapping channels, making it easier to choose the appropriate one.
If the "Auto" setting isn't delivering satisfactory results, sign into your router's administrator interface and go to the basic wireless category. Try manually selecting a channel, ideally one that isn't used by many networks in your area. Conduct another speed test to check whether it provides a better signal and faster speeds in your problem areas compared to the "Automatic" setting.
Note that channel congestion can change over time. If you manually select a channel, you should periodically check to ensure that it's still the most suitable option.
Kick leeches off your Wi-Fi
The cause of your Wi-Fi problems may not be interference or range-related. If your network is open or has a weak password, you could have unauthorized users leeching off your network. If a neighbor is streaming multiple 4K movies on your Wi-Fi, it will impact your video chats. Tools such as Wireless Network Watcher can help you detect all the devices connected to your network and expose neighbors who may be stealing your Wi-Fi. Your router's admin interface may also include a traffic analyzer that can identify which devices are consuming excessive data.
You may even discover that one of your children is using up your bandwidth without your knowledge. If that's the case, you can learn how to remove them from the network.
After you've identified the intruder and fixed the issue, it's essential to secure your network with a robust password. It's best to use WPA2 encryption because WEP is easy to crack, allowing others to join your network.
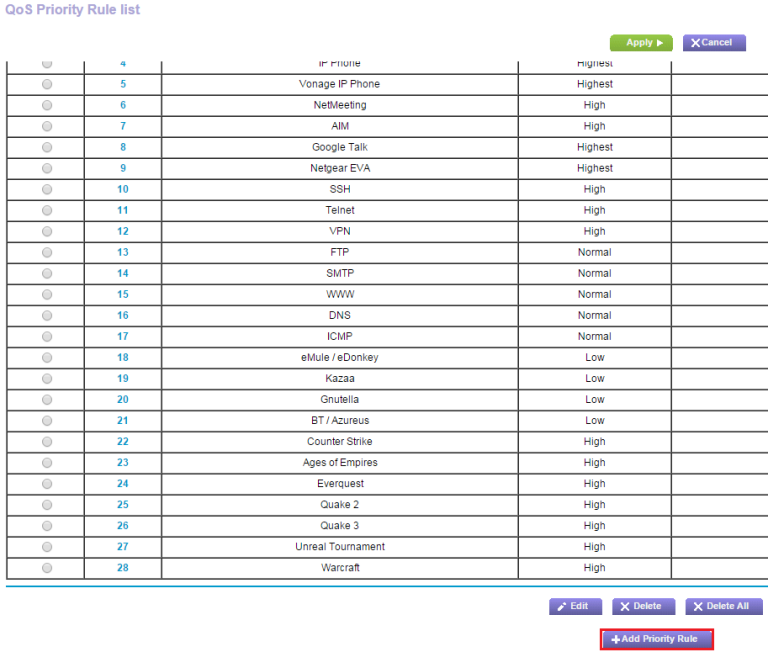
Quality control
Modern routers typically come equipped with Quality of Service (QoS) tools to help manage bandwidth usage. These settings can usually be found under advanced settings in the network's admin interface, such as the Netgear menu shown above. With QoS, you can prioritize certain types of traffic over others. For instance, you could prioritize video calls over file downloads to ensure that your call with your grandmother won't suffer just because someone else is downloading a large file. Although the file download may take longer, the video call should remain stable. Some QoS settings even allow you to prioritize different apps during specific times of the day.
Some routers even offer a one-click multimedia or gaming setting to make it easier to prioritize these types of traffic. If you're trying to stream games while sharing a network, there are additional steps you can take to improve your experience.
Get rid of old hardware components
It's important to make the most of the equipment you have, but if you're working with older hardware, you can't expect top-notch performance. When it comes to back-end devices like networking gear, we often subscribe to the "if it ain't broke, don't fix it" mentality. However, if you've had your router for several years, you may still be using the older, slower 802.11n standard (or even worse, 802.11g).
These older routers have limitations when it comes to bandwidth and range. For example, 802.11g has a maximum throughput of 54Mbps, while 802.11n caps out at 300Mbps. All the tweaks we've discussed so far can only do so much for these outdated models. But if you upgrade to a new router with the latest 802.11ac standard, you'll have support for 1Gbps. Next-gen Wi-Fi 6 routers can theoretically reach speeds of 10Gbps, and Wi-Fi 6E routers have access to even more spectrum that can provide additional coverage.

Try a range extender
If you've tried all the previous solutions and still can't seem to get a strong Wi-Fi signal throughout your entire house, it's possible that your home is just too large for a single router to handle. Your router may also be struggling to penetrate all the walls and corners of your house. In this case, you might need to consider adding a range extender or investing in a mesh network.
A range extender can pick up your router's signal and amplify it to extend your network's reach. While range extenders can be a budget-friendly solution, they're often not as effective as mesh Wi-Fi systems. Mesh networks, on the other hand, replace your existing router entirely and use multiple units to intelligently route traffic back to your modem, creating a seamless Wi-Fi network that covers every corner of your home.
When setting up a mesh network, you'll want to follow the same placement rules as with your router and range extender: one node should be connected to your modem, and each additional node should be placed close enough to pick up a strong signal while far enough to extend coverage to areas with poor signal strength.
Related: How to stay safe while using public Wi-Fi

Speed up your network easily
There are many ways to improve the performance and coverage of your Wi-Fi network. From updating your router's firmware and optimizing its settings to choosing the right channel and placement, there are many things you can do to ensure a strong and reliable connection. If all else fails, consider adding external antennas or investing in a range extender or mesh network to extend your signal. By following these tips and tricks, you can enjoy a faster and more stable Wi-Fi connection for all your internet needs.
Thank you for being a Ghacks reader. The post How to Boost Your Wi-Fi Signal for Better Internet Speeds appeared first on gHacks Technology News.
0 Commentaires