Wikipedia has revealed that it is seeing a decline in web traffic from human users. And the reason for it is, unsurprisingly, AI search.
An article posted by Wikimedia Foundation's Marshall Miller highlights how global trends have negatively impacted Wikipedia. The article says that Wikimedia Foundation's algorithms classify traffic from humans and bots. In May 2025, the foundation observed unusually high amounts of seemingly human traffic from Brazil. After investigating the matter, it updated its bot detection systems. Then the traffic data was reclassified for March to August 2025. It appears that a lot of the traffic was actually bots that were designed to evade detection.
The analysis reveals that Wikipedia saw a drop in human user traffic of around 8%, for the same duration, compared to 2024. Wikimedia believes that this decline is due to the bots, which are due to generative AI summaries on search engines, chatbots and social media. It says that Wikipedia's data sets are used to train almost all large language models (LLMs), but they may not always link to its sites. The report also notes that this behavior is not unique to Wikipedia, other platforms, publishers are observing the same.
You may recall that Google has previously denied that AI in search results in less traffic, as in it does not steal traffic from blogs and other websites, contrary to reports that said Google AI Overviews has over 2 Billion monthly users.
. Well, here is solid proof that's not the case, and this is coming from a company whose business is entirely dependent on web traffic.
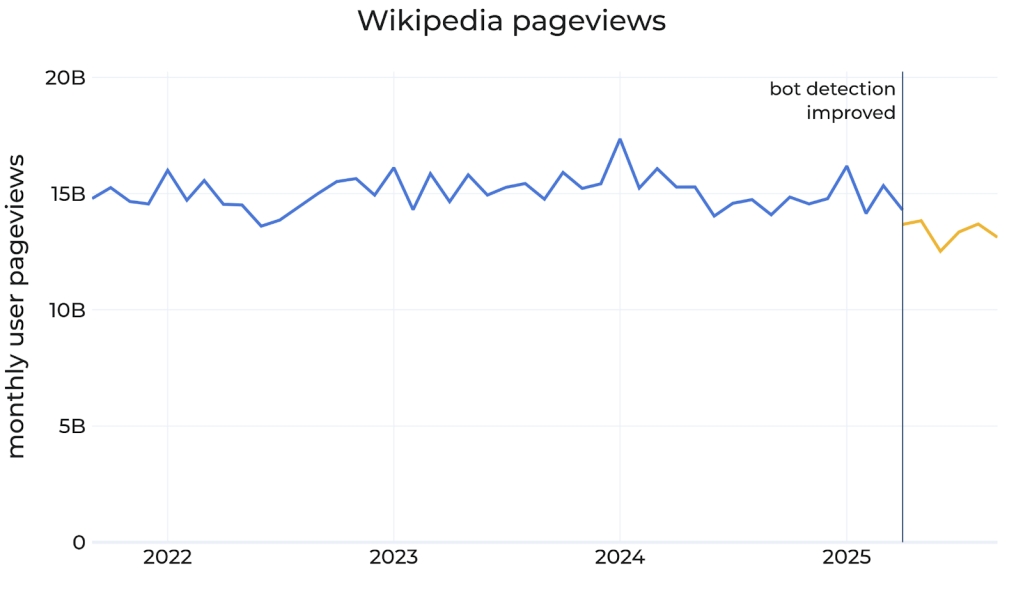
(Image courtesy: Wikimedia)
When a user finds what they want from an AI, they don't visit the source, or continue with that session. This results in a loss of traffic for the source.
As TechCrunch reports, Wikipedia itself had experimented with AI-generated summaries in June, and drew criticism from editors. It's unethical.
Don't get me wrong. AI search offers a lot of value, it can save you a lot of time depending on the topic that you are researching. Personally, I have found AI search useful for specific scenarios like shopping, searching for coupons, pulling up product information, terms and conditions, etc., that may be buried deep on a website that doesn't really show up on a regular search.
However, the problem is that the quality of AI search results is often not better than a traditional search engine. Bots may spit out a summary based on low-effort posts, inaccurate content, fabricated posts on social media, etc. How many people take the time to verify the results? Not a lot I guess, they just assume whatever the AI says is true, which can often be misleading, as a lot of the things that you across on the web are themselves AI-generated. Such inaccuracies are often called "hallucinations", which I find to be a bit misleading. AI models are not sentient, they are trained on datasets. If it can't think on its own, it cannot hallucinate. They just reproduce information, not create them.
AI in search needs to be improved, and ensure websites are credited with proper links. Wikipedia is encouraging AI users to visit the source material. It is working on 2 new readers teams called Reader Growth and Reader Experience), in order to improve the ways users access Wikipedia, and is also working on a framework for attribution, among other improvements.
Thank you for being a Ghacks reader. The post Wikipedia sees decline in human pageviews, says AI is to blame appeared first on gHacks Technology News.


0 Commentaires